Switches | Outlets & Plugs | Ballasts | Replace Ballasts | LED Tube Lights | Troubleshooting | Basic Electricity | Misc Articles
About Privacy Policy Sitemap Copyright © 2024 Electrical101.com Terms of Use
Basic Electricity
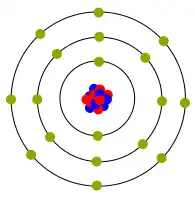
Conductor Atom
Insulator atom
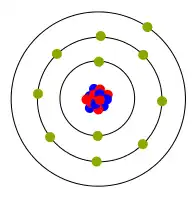
Single electron in outer orbit
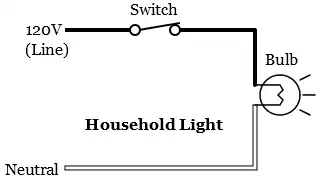
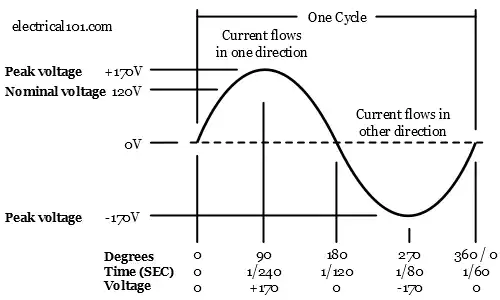
Current flows in both directions. 120 VAC 60 Hz household power is an example of AC current. There are two changes in polarity and two changes in current direction per cycle. The current in 120 VAC 60 Hz changes direction 120 times per second as shown below.
Direct and Alternating Current
At 0 degrees the voltage is at 0 volts and starts to rise to a peak voltage of 170 volts at 90 degrees. At 90 degrees the voltage goes back down to 0 volts at 180 degrees. The current then reverses direction and rises to a peak voltage of -
Conductor and Insulator Properties
- The nucleus (center) of an atom contains protons and neutrons. Electrons orbit around the nucleus.
- The atoms of conductive material have single (or few) electrons in the outer orbit called Valence Electrons. They are situated so they can be moved from one atom to another easily and enhance the movement of electrons. Copper is a good conductor and is used for most wires.
- An insulator has many (7-
8) electrons in the outer orbit, these electrons are very difficult to move from one atom to the other and resist the movement of electrons.
An electrical current (the movement of electrons) happens when there is a potential difference (voltage) between the ends of a conductor.
Multiple electrons in outer orbit
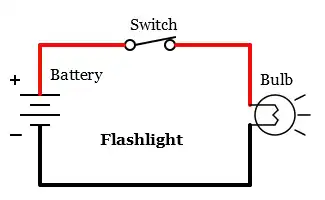
Current flows in one direction. A battery operated flashlight is a very common example of direct current.
Alternating Current (AC)
Direct Current (DC)

Basic Electricity
120V 60 Hz Sine Wave Diagram